Newtec Power Equipment Co., Ltd.
English

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-05 Origin: Site
Power generators have become essential for homes, businesses, and outdoor activities. Power outages, storms, or remote locations can leave you without electricity, making it crucial to have a reliable power generator. Understanding the three types of power generators—standby, portable, and inverter—helps you choose the right unit for your specific needs. Each type has unique features, fuel requirements, and advantages, whether you need full-home backup, temporary power, or clean, stable electricity for sensitive devices. In this guide, we’ll explore how these power generators work, their benefits, and what to consider before making a purchase.
A power generator is a device that converts fuel into electricity, providing power when the main electrical supply is unavailable. This type of power generator can serve as backup power during outages or as the primary electricity source in remote locations. Power generators use a variety of fuel types, including gasoline, diesel, propane, natural gas, solar energy, and even hydrogen. Inside the power generator, fuel is converted into mechanical energy by the engine, which is then transformed into electrical energy to power appliances, tools, and electronics. Some power generators, such as inverter models, also regulate the current to deliver clean and stable electricity for sensitive devices.
Generators ensure that your home or business stays powered when the grid fails unexpectedly. They keep lights, refrigerators, heating or cooling systems, and other essential appliances running, preventing disruptions during storms, maintenance work, or blackouts. They are also crucial for outdoor and mobile applications, such as powering construction tools, camping equipment, or outdoor events. Businesses and medical facilities rely on generators to maintain operations, support safety systems, and protect sensitive equipment. Additionally, modern generators allow safe charging of laptops, phones, and other electronics without the risk of power surges or damage.
Generators come with a variety of features that determine how effectively they can meet your power needs:
Power Output – Measured in kilowatts (kW), this determines how many appliances, devices, or tools the generator can run at the same time. Larger homes or businesses require higher output.
Fuel Type and Efficiency – Generators can run on gasoline, diesel, propane, natural gas, solar, or hydrogen. Some models adjust engine speed according to load, which saves fuel and reduces costs over time.
Noise Levels – Noise varies widely depending on design and fuel. Inverter generators and enclosed models are much quieter than traditional diesel or open-frame units.
Portability – Generators can be stationary or mobile. Portable units are easy to move between sites, while standby units are installed permanently for continuous power.
Safety Features – Modern generators may include automatic shutoff, overload protection, or voltage stabilization to protect sensitive electronics and prevent accidents.
Additional Features – Some models offer remote monitoring, eco-modes for fuel savings, or automatic start during outages, making operation more convenient.
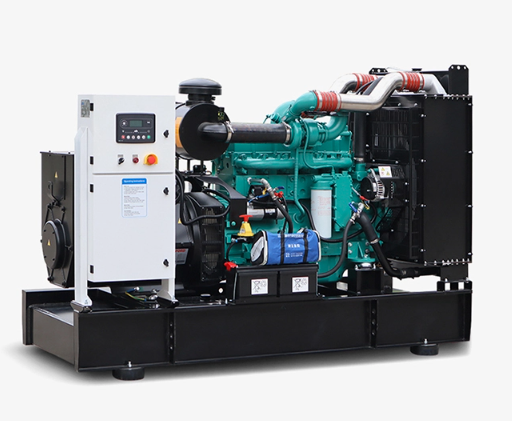

Standby generators are permanent installations outside homes or businesses. They automatically detect when the main power goes out and start running without any manual effort. Most standby generators run on natural gas or propane, providing a steady, uninterrupted power supply. They are capable of powering an entire household or business, including lighting, heating and cooling systems, refrigerators, kitchen appliances, security systems, and even medical equipment. Larger models can run continuously for several days, as long as fuel is supplied.
Standby generators are highly reliable and convenient. They remove the need for extension cords or manual startup, making them ideal for critical applications. However, they have higher upfront costs due to both the generator and professional installation. Regular maintenance—typically twice a year—is essential to ensure they operate correctly when needed. Fuel supply must be monitored, as these units rely on constant access to propane or natural gas. Despite the cost, they are the preferred choice for full-home backup, medical facilities, or industrial sites where uninterrupted power is crucial.
Portable generators are compact, movable units designed for temporary power needs. They usually run on gasoline, diesel, or propane and can provide electricity to small appliances, power tools, or emergency equipment. Their mobility makes them perfect for camping trips, outdoor events, construction sites, or home emergencies. Most portable generators include built-in outlets for direct connections, and some models can be wired to a home sub-panel to power multiple appliances simultaneously.
The main advantages of portable generators are affordability and flexibility. They can be moved easily to wherever power is needed and are simple to operate. However, limitations include manual startup, outdoor-only usage due to carbon monoxide risks, and lower total power output compared to standby units. Sensitive electronics may require a voltage stabilizer or inverter attachment to prevent damage. Despite these limitations, portable generators remain an accessible and practical solution for temporary or on-the-go power requirements.
Inverter generators use advanced technology to produce clean, stable electricity by converting AC → DC → AC. This process delivers low total harmonic distortion (THD), making the power safe for sensitive electronics such as laptops, smartphones, TVs, and audio equipment. These generators are compact, lightweight, and quiet, with engines that automatically adjust speed to match power demand. This improves fuel efficiency and reduces noise, making them suitable for home use, camping, RVs, and boats.
Inverter generators are praised for their stable voltage, quiet operation, and fuel efficiency. They are ideal for smaller-scale applications or for powering sensitive electronics safely. However, they have a higher purchase price and lower maximum power output than large standby units. Maintenance is simpler than for diesel or large standby generators, but routine checks of oil, fuel, and air filters are necessary. For those who prioritize portability, clean electricity, and quiet performance, inverter generators provide a reliable and flexible power solution for both residential and recreational use.
| Feature | Standby Generator | Portable Generator | Inverter Generator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | High (7–22 kW+) | Low to medium (1–10 kW) | Low to medium (1–5 kW) |
| Portability | Stationary | Easy to move | Compact and lightweight |
| Noise Level | Moderate to high | High | Low |
| Fuel Type | Propane, Natural Gas | Gasoline, Diesel, Propane | Gasoline, Diesel |
| Sensitive Electronics | Yes (needs stabilizer) | Sometimes (needs stabilizer) | Safe |
| Cost | High | Affordable | Moderate to high |
| Best Use Case | Full-home backup | Temporary or mobile power | Electronics & quiet operation |
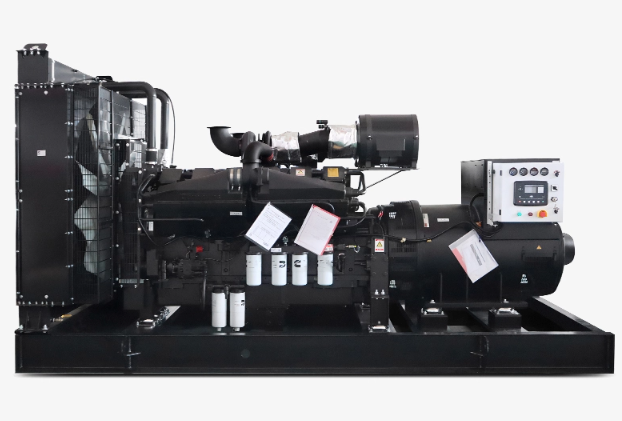
Before buying a power generator, calculate how much electricity you actually need. Make a list of essential appliances and devices you want to power during an outage—refrigerators, heating/cooling systems, lights, medical equipment, or electronics. Add up their wattage to determine the total load. Choosing a generator that can handle peak demand ensures all your devices run smoothly without overloading the unit.
Generators run on various fuel types: gasoline, diesel, propane, natural gas, solar, or even hydrogen. Check what fuels are easily accessible in your area. If you prefer a low-maintenance option, natural gas or propane might be ideal. Diesel generators are efficient and long-lasting but require fuel storage. Solar-powered generators reduce fuel costs and emissions but need sunlight and may not power large appliances for extended periods.
Some generators are loud, which can be disruptive in residential areas or shared spaces. Standby generators are generally louder but operate outside, while inverter generators are quieter and more suitable for homes, RVs, or camping. Consider the environment and noise regulations when choosing your generator.
Factor in more than the purchase price. Include installation, fuel, and maintenance costs. Standby generators are more expensive upfront and require professional installation, while portable and inverter generators are cheaper and easier to set up. Long-term costs, such as fuel efficiency and replacement parts, can impact overall affordability.
Will your generator stay in one place, or do you need it on the move? Standby generators are permanent, whereas portable and inverter generators can be relocated. Portable units are ideal for temporary needs, while inverter generators combine portability with clean, stable power for sensitive electronics.
A power generator can be hazardous if used incorrectly. Always ensure proper ventilation to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning. Ground the generator to prevent electrical shock, and store fuel safely. Follow manufacturer instructions for maintenance and operation to ensure safe and reliable power during emergencies.
Always operate outdoors, away from windows, doors, and vents to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Avoid overloading; check wattage limits and prioritize essential appliances.
Maintain regularly by changing oil, cleaning filters, and inspecting fuel lines.
Store fuels safely in approved containers, away from heat and children.
Use transfer switches when connecting to home electrical panels to prevent backfeed and allow safe power distribution.
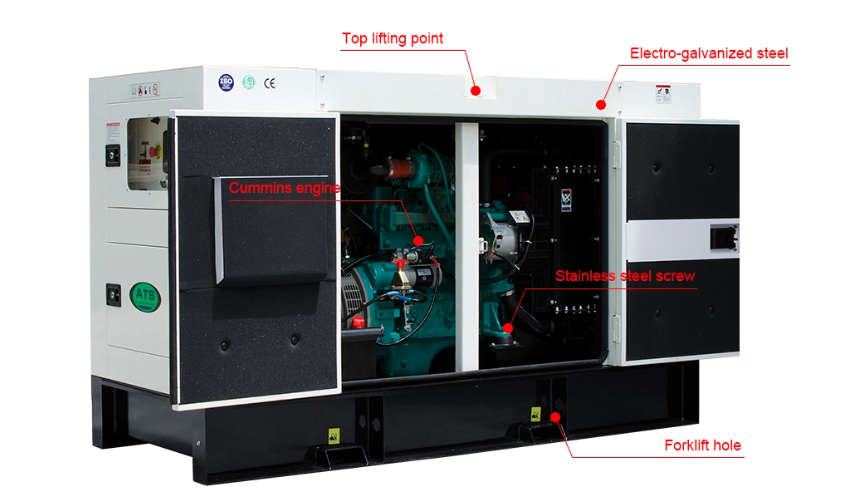

Portable generators usually provide enough power for essential appliances but rarely cover an entire home. Standby generators are better suited for full-home backup.
Yes, inverter generators produce stable, clean electricity that prevents voltage spikes, making them safe for laptops, phones, TVs, and other sensitive devices.
Maintenance frequency depends on the type and usage, but most generators require at least biannual service, including oil changes, filter cleaning, and fuel checks.
Noise levels vary: standby generators produce moderate to high noise, portable units can be loud, and inverter generators are quiet, suitable for residential or recreational use.
Choosing the right power generator ensures safety, convenience, and uninterrupted power for your home or business. Standby generators provide full-home backup, portable units offer flexibility for temporary needs, and inverter generators deliver clean, quiet energy for sensitive electronics.
By assessing your power generator needs, fuel options, budget, and portability requirements, you can select a unit that fits your lifestyle perfectly. For reliable, high-quality power generators and expert support, trust Newtec Power Equipment Co., Ltd. to provide solutions that keep your electricity flowing when you need it most.